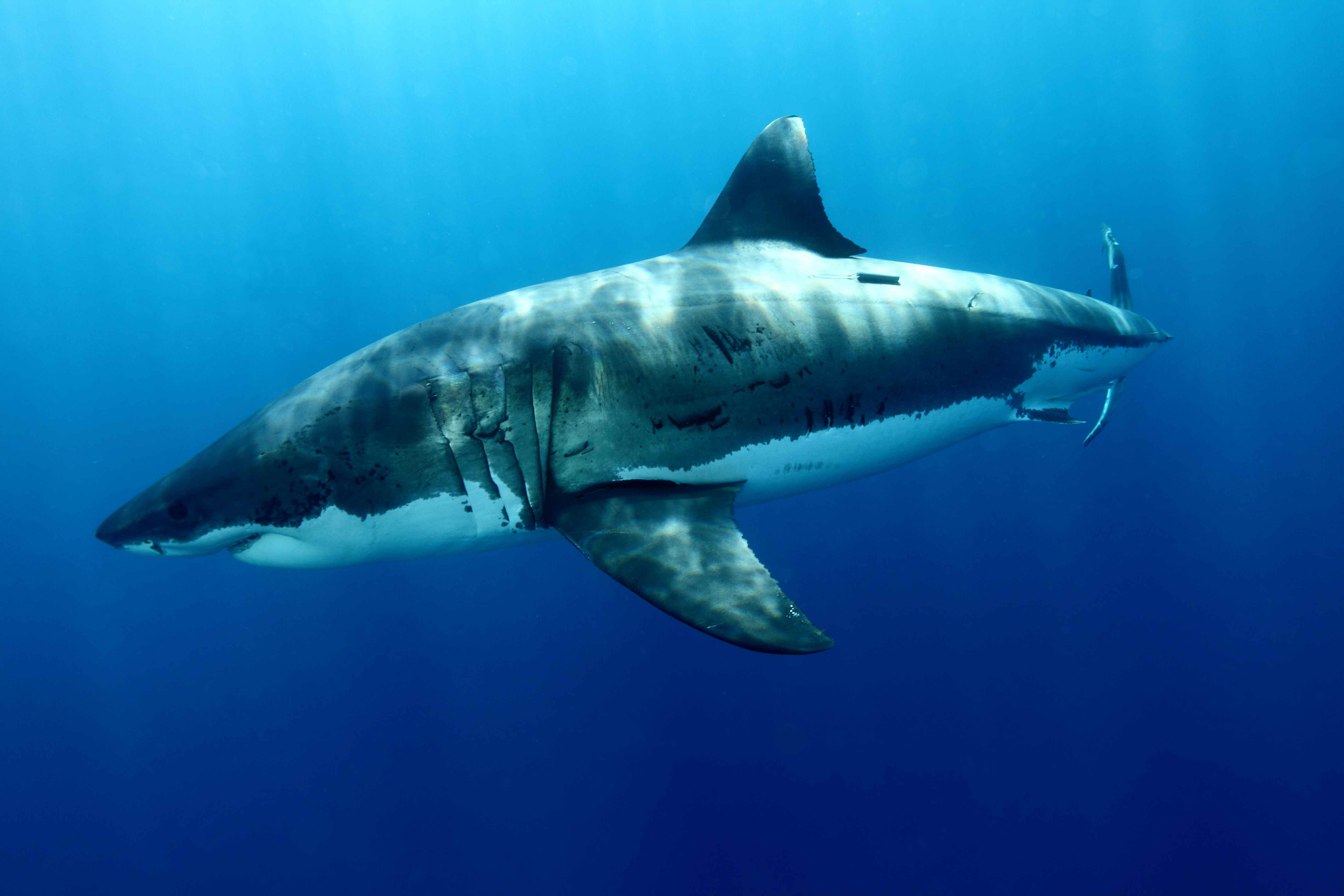
Great White Sharks are making headlines this summer, as sightings along the northern Atlantic Coast soar, signaling a shift in their habitat patterns. The dramatic increase in the Great White shark population off the coast of New England has captured the attention of marine experts and beachgoers alike, especially in areas previously untouched by these formidable predators. The Maine Department of Marine Resources recently identified a record 93 Great White Sharks in its waters, raising awareness of shark conservation efforts and the importance of protecting these incredible animals. This surge in shark sightings also plays into community concerns following incidents such as the tragic Maine shark attack in 2020, reminding us of the delicate balance between human activity and marine wildlife. With the Atlantic White Shark Conservancy leading initiatives to study and help sustain these sharks, understanding their presence has never been more crucial.
The resurgence of large predatory fish, often referred to as apex predators, brings attention to the growing presence of these magnificent ocean dwellers in northern waters. Known for their stunning power and grace, these ocean giants have started migrating to areas like New England, where sightings were once rare. As environmental conditions shift and conservation measures gain traction, the population of these remarkable creatures is on the rise, prompting both excitement and caution. Recent events, including a tragic attack in Maine, have shed light on the need for heightened awareness regarding shark conservation. As we delve into this topic, it is essential to recognize the balance between thrill-seeking adventures along our coastlines and the imperative commitment to protect and understand the complexities of marine ecosystems.
The Rise of Great White Shark Sightings in New England
Recent years have witnessed an unprecedented rise in Great White Shark sightings along the New England coast, an area once considered relatively safe from these apex predators. In a surprising twist reminiscent of the blockbuster ‘Jaws,’ the real waters of New England have become the backdrop for increased shark encounters. Reports indicate that from 2020 to 2024, the Maine Department of Marine Resources (DMR) identified 93 individual Great White Sharks. This surge in sightings not only captivates the excitement of wildlife enthusiasts but also raises concerns regarding marine safety and shark conservation.
The exact reasons for this remarkable increase in Great White Shark presence are multifaceted. Studies indicate that warmer sea temperatures in the Gulf of Maine are leading these migratory sharks to expand their summer habitats into cooler northern waters. Incredibly, data from the Atlantic White Shark Conservancy (AWSC) suggests that conservation efforts, including protective regulations for seals, which are a primary prey for these sharks, have significantly contributed to their growing populations in the region. The increase in shark sightings offers a unique opportunity for education and awareness about marine ecosystems, yet it also emphasizes the importance of safe coexistence with these powerful creatures.
Understanding Shark Conservation Efforts
Shark conservation has evolved significantly over the years, with organizations like the Atlantic White Shark Conservancy (AWSC) leading many essential initiatives aimed at safeguarding the species and their habitats. By focusing on research, public education, and policy advocacy, the AWSC plays a pivotal role in fostering a deeper understanding of shark behavior, migration patterns, and the importance of biodiversity within marine ecosystems. Their efforts not only facilitate a more profound respect for sharks but also encourage the protection of entire ocean habitats which are critical to the balance of marine life.
Additionally, the increase in Great White Shark sightings has propelled discussions surrounding the importance of maintaining ecological balance. From rehabilitating coastal habitats to implementing regulations against overfishing, today’s shark conservation efforts are critical as they focus on restoring population numbers for many species. By reinforcing protective measures for sharks and their food sources, conservationists are paving the way for healthier marine environments. These initiatives can lead to a ripple effect, positively impacting the overall health of ocean ecosystems, thus benefiting the sharks and their surrounding habitats.
The Impact of Rising Sea Temperatures on Shark Behavior
The implications of rising sea temperatures on Great White shark behavior cannot be understated, particularly as these changes have prompted sharks to migrate further north than ever before. Recent research highlights that the Gulf of Maine is experiencing temperature increases faster than 99% of the global oceans, altering the natural lifecycle and migration patterns of these sharks. As a reaction to warmer waters, Great Whites are prolonging their stays in northern habitats, significantly altering the dynamics of local marine life.
This migration trend raises important questions about the future of shark populations and their interactions with coastal communities. Given that these apex predators usually migrate south to escape harsher winters, their extended presence in New England may be linked to climate change effects. As these sharks adapt to changing environmental conditions, it is essential for researchers, conservationists, and community members to engage in proactive measures to understand these movements. By prioritizing further research into the impacts of climate change on marine life, stakeholders can develop more strategic conservation plans that align with the evolving nature of shark populations.
Maine’s Historic Shark Attack and Its Aftermath
The rare occurrence of a shark attack in Maine sent shockwaves through the community, notably following the tragic incident in July 2020 when a swimmer lost her life off the coast. This fatal incident marked only the second recorded shark attack in Maine since 1837, highlighting the extremely low likelihood of shark encounters leading to attacks. The Maine Department of Marine Resources has taken crucial steps in the aftermath of the event by implementing emergency bleed kits on beaches to assist potential victims. These precautionary measures reflect a growing recognition of the changing dynamics of shark populations looming over historical perceptions of safety in the water.
Despite the dramatic implications associated with such rare incidents, experts like Gavin Naylor of the Florida Museum of Natural History underscore that shark attacks remain exceedingly rare occurrences. Sharks typically avoid interaction with humans, and the public often swims unaware that sharks are present, with many staying offshore. Such perspectives are essential in alleviating public fears and reinforcing the idea that conservation and respect for these creatures can promote coexistence rather than conflict between sharks and coastal communities.
Shark Encounters: Rare but Increasingly Documented
Shark encounters, while infrequent, are becoming more documented due to the recent uptick in sightings along the Atlantic Coast. Reports indicate a significant rise in interactions and encounters, primarily related to increased shark populations and evolving patterns of behavior. The International Shark Attack File (ISAF) data highlights that, although the United States continues to have the highest number of unprovoked shark bites globally, the actual instances remain below the five-year average. This underscores the uniqueness of these predatory interactions and the importance of understanding the factors that contribute to them.
As interest in shark encounters grows, so too does the responsibility to enter into informed discussions regarding safety and conservation. Increased awareness of sharks’ role in the marine ecosystem necessitates educational campaigns directed at beachgoers and ocean enthusiasts. The need for understanding even the most sensational shark stories, such as depicted in films like ‘Jaws,’ is vital to prevent misinformation and fear surrounding these species. Ultimately, fostering awareness about their ecological importance can shape public perception and promote supportive conservation efforts.
Integrating Shark Conservation into Coastal Management
As shark sightings continue to increase along the Atlantic Coast, coastal management strategies must integrate shark conservation into their frameworks. By combining effective fisheries management, habitat protection, and public safety initiatives, local governments can help create safe environments for both humans and wildlife. Approaches may include the establishment of protected marine areas where sharks can thrive without disturbances, encouraging ecosystem recovery while placing a focus on advocating responsible tourism and recreation.
The balance between human activity and wildlife conservation is vital as coastal regions become more populated. Officials must encourage sustainable practices that contribute positively to shark populations while addressing the safety concerns of residents and visitors. Adopting measures that incorporate public engagement and community education on the importance of sharks can help create a society that values coexistence with these majestic creatures, ultimately leading to healthier marine environments.
Public Education on Shark Safety and Awareness
Educational outreach plays a pivotal role in shaping public perception about sharks, especially given the fascination and fear stemming from cultural references like ‘Jaws.’ By providing accurate information about shark behavior, migration, and the rarity of attacks, shark conservation groups emphasize the significance of understanding and respecting these remarkable creatures in their natural habitats. Such education equips the public with knowledge about what to do in the rare event of an encounter, fostering safer ocean experiences for beachgoers.
Organizations are developing resources for local communities to articulate not only the threats sharks face but also their ecological importance. Increased public awareness about the conservation efforts by groups like the Atlantic White Shark Conservancy can inspire individuals to participate in marine safety campaigns and advocacy efforts. Collaborating with schools and local organizations fosters a more informed and responsible population, ultimately leading to stronger support for ongoing shark conservation initiatives.
Future Research Needs in Shark Conservation
To effectively safeguard shark populations, ongoing research is critical in illuminating the changing dynamics driven by environmental factors. Future studies must focus on the impacts of climate change on migration patterns, breeding behaviors, and ecological roles of sharks in their respective habitats. By understanding these facets, conservation strategies can be better tailored to the specific needs of different shark species, allowing for more effective management and protective measures in response to current trends.
Collaborative efforts among scientists, researchers, and conservation organizations will pave the way for innovative data collection techniques that can monitor shark populations more accurately. Increased technological advancements, such as tagging and remote monitoring, will yield valuable insights into shark behavior and their interactions with various marine environments. Support for such initiatives demonstrates a commitment to responsible stewardship of ocean ecosystems and ensures that the burgeoning Great White shark population can be managed sustainably for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are recent shark sightings of Great White Sharks along the northern Atlantic Coast?
Recent shark sightings of Great White Sharks have been increasing along the northern Atlantic Coast, particularly in cooler waters off New England, including Maine. Between 2020 and 2024, the Maine Department of Marine Resources identified 93 Great White Sharks in this area, signaling a rise in their population.
What is the significance of the Maine shark attack in understanding Great White Sharks?
The Maine shark attack in July 2020 marked a critical moment in understanding Great White Sharks’ behavior in the region, as it was the first fatal attack recorded in the state. This incident has prompted increased tracking and conservation efforts, emphasizing the need for awareness and safety in areas where shark populations are rising.
How does the Great White shark population relate to shark conservation efforts in the Atlantic?
The increasing Great White shark population along the Atlantic coast can largely be attributed to effective shark conservation efforts by organizations like the Atlantic White Shark Conservancy. These efforts focus on protecting shark habitats and their seal prey, contributing to a healthier ecosystem in which sharks can thrive.
What findings have studies revealed about the Great White shark population off the coast of Halifax?
Studies have shown that the Great White shark population off the coast of Halifax, Nova Scotia, has increased by approximately 2.5 times from 2018 to 2022. This growth reflects changing marine conditions and highlights the significance of ongoing shark conservation efforts in the area.
What measures have been implemented in Maine following the first shark attack involving a Great White?
In response to the first fatal shark attack in Maine involving a Great White, the state has installed emergency bleed kits on coastal beaches for first-aid support. Additionally, tracking of Great White shark movements has been initiated to monitor their populations and enhance public safety.
Why are shark sightings of Great White Sharks becoming more frequent in Long Island?
Shark sightings of Great White Sharks in Long Island are becoming more frequent due to multiple factors, including rising ocean temperatures and successful shark conservation initiatives. These conditions have led to sharks migrating northward and staying in the area longer during warmer months.
What is the connection between rising sea temperatures and the Great White shark population in the Gulf of Maine?
Rising sea temperatures in the Gulf of Maine are significantly impacting the Great White shark population, as these sharks are being observed remaining in cooler waters longer due to climate change. This trend suggests that warmer waters may be affecting their migratory patterns and behaviors, contributing to more sightings along the northern Atlantic Coast.
How common are shark attacks involving Great White Sharks in the United States?
Shark attacks involving Great White Sharks remain very rare in the United States. According to the International Shark Attack File, the total number of unprovoked shark bites has been below the average in recent years, with the 2024 report indicating that while there were confirmed attacks, they are still uncommon occurrences.
What role does the Atlantic White Shark Conservancy play in shark conservation efforts?
The Atlantic White Shark Conservancy plays a critical role in shark conservation efforts by conducting research, raising public awareness, and implementing protective measures for Great White Sharks and their habitats. Their work is essential in monitoring shark populations and promoting safe coexistence between humans and sharks.
What impact did the movie ‘Jaws’ have on public perception of Great White Sharks?
The movie ‘Jaws’ significantly impacted public perception of Great White Sharks, instilling fear and a misconception that these sharks are aggressive towards humans. However, actual shark attacks are exceedingly rare, and the perceptions shaped by the film often overlook the ecological importance of sharks in marine environments.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Great White Sharks are increasingly sighted along the northern Atlantic Coast. |
| Recent data indicates they are found more frequently in cooler waters off New England. |
| From 2020-2024, Maine identified 93 Great White Sharks off its coast. |
| The increase may be linked to conservation efforts as well as rising sea temperatures. |
| Shark attacks are extremely rare, with only two recorded in Maine since 1837. |
| Despite the fear surrounding them, sharks typically avoid humans and usually remain offshore. |
| Florida still registers the highest number of unprovoked shark attacks in the U.S. |
Summary
Great White Sharks are experiencing a notable surge in populations along the northern Atlantic Coast, particularly in areas like Maine and Long Island. This increase is largely attributed to a combination of conservation efforts and climatic changes affecting their migratory patterns. Although the increased sightings have raised public awareness and alarm, it is essential to understand that shark attacks remain exceedingly rare. By promoting education and understanding about these magnificent creatures, we can foster coexistence and appreciate their vital role in our marine ecosystems.