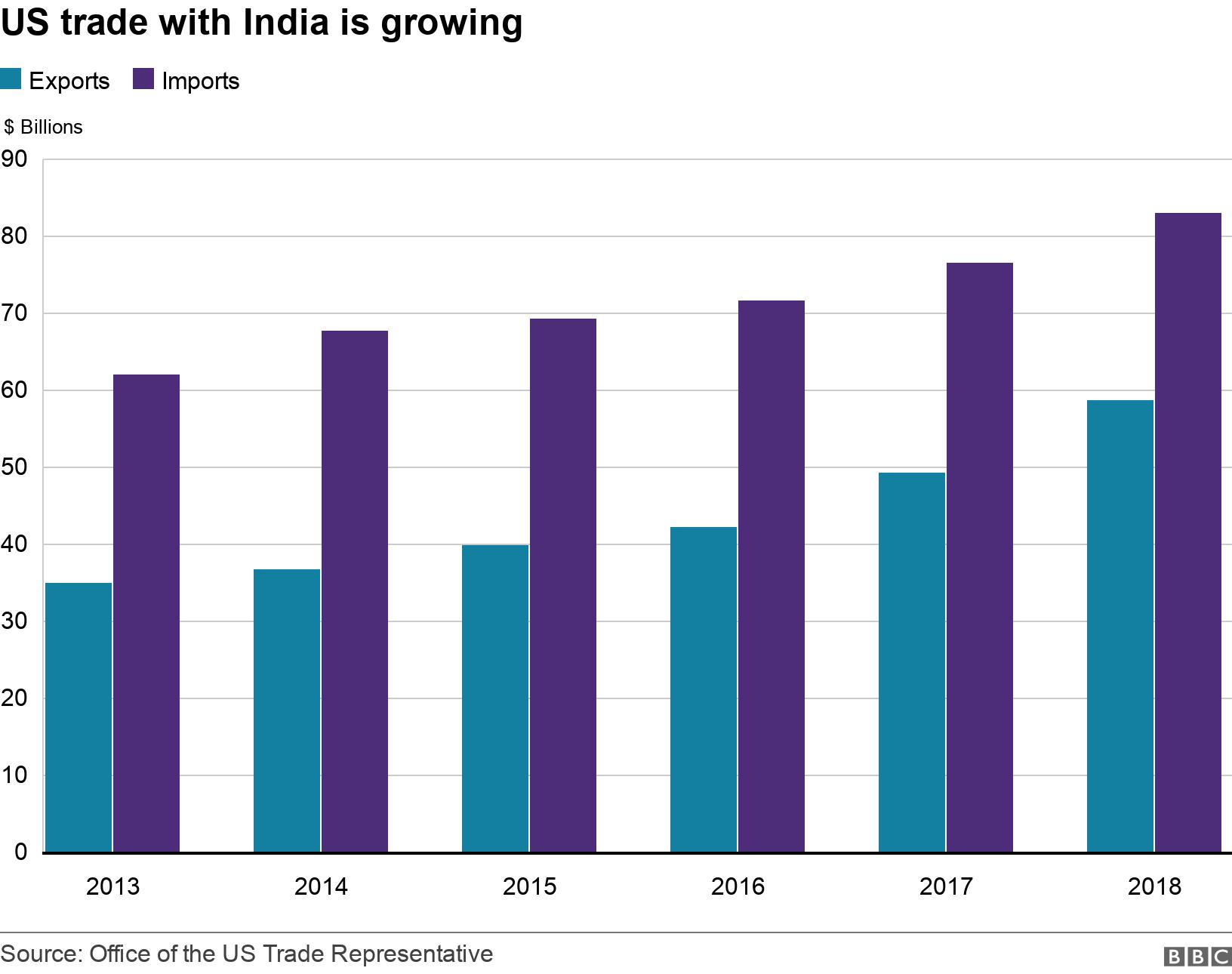
In a significant shift in US trade policy, the recent imposition of elevated tariffs on Indian imports has become a focal point of economic discussion. The US tariffs on Indian imports have surged to unprecedented levels, doubling to 50%, with potential impacts rippling through American consumers who rely on a variety of goods from India, including textiles and seafood. This steep levy, initially introduced as part of the Trump tariffs on India, poses real challenges for sectors like shrimp farming and apparel manufacturing, where price hikes could soon be felt at grocery stores and clothing retailers. Businesses are now reassessing their supply chains in light of these changes, as American companies are increasingly seeking alternatives to Indian sources. As the landscape of international trade shifts, the repercussions of these tariffs may redefine markets and consumer options across the United States.
The recent hike in import duties from the US on goods brought in from India marks a pivotal moment in international trade relations. Known broadly as tariffs on Indian commercial products, these tax increases have immediate implications not only for exporters in India but also for consumers in America. The reconfiguration of trade routes could lead to a notable disruption in the availability and pricing of various imports, particularly essential items like textiles and seafood. As businesses scramble to adjust to new economic pressures, there exists a potential for altered consumer costs that could reshape purchasing behaviors. Overall, these developments urge a closer examination of how changing trade policies affect global markets and everyday life.
Impact of US Tariffs on Indian Imports
The recent decision by President Trump to increase tariffs on Indian imports has sent ripples through the U.S. economy, primarily affecting American consumers. With tariffs on textiles and seafood jumping to an unprecedented 50%, prices for these essential goods are projected to climb. As many households rely on imports from India, the price hikes could have a significant impact on everyday expenses, especially for families that purchase clothing and food items from Indian suppliers.
Furthermore, the tariffs are more than just a financial burden; they symbolize a shift in US trade policy toward greater protectionism. This strategy could inadvertently lead to a decrease in the diversity of products available to consumers and push businesses to seek sourcing alternatives in countries facing their own trade barriers. While the tariffs aim to pressure India over its dealings with Russia, the broader consequences may well harm American shoppers who have come to depend on competitively priced Indian goods.
Effects on Indian Seafood Exports
The seafood industry, particularly shrimp farming in India, has begun to feel the effects of raised tariffs significantly. Originally exporting shrimp to the U.S. with minimal barriers, Indian suppliers now face additional 25% tariffs that have recently jumped to 50%. This drastic increase is anticipated to push prices higher for American consumers seeking seafood options, particularly among imported varieties. With consumers unable to avoid these raises, this segment of the market could experience a shift as buyers turn to alternate sources like Ecuador or Vietnam.
Moreover, the overall volume of seafood exports from India is expected to drop sharply. A recent report indicated that Indian seafood exports could plunge to below $50 billion in the near future. This scenario underlines not only the immediate economic implications for Indian farmers but also highlights the interconnected nature of global trade. As U.S. trade policy tightens, American consumers may begin to notice these changes at the checkout aisle, affecting how and what seafood options are available.
Impact on American Textiles and Apparel
The textile and apparel sectors could potentially suffer the most from the newly enforced tariffs. Given that the U.S. market relies heavily on Indian textiles—representing over 35% of total exports—this sudden shift will likely force manufacturers and retailers to adjust their sourcing strategies. With American households already facing inflation, higher tariffs on textiles will result in elevated clothing prices, as companies may look elsewhere for cheaper production, possibly turning to Bangladesh or Vietnam.
Industry experts have warned that the repercussions of these tariffs could extend further, impacting employment in India’s textile sector. The sudden imposition of such high tariffs places immense pressure on Indian manufacturers, threatening local job opportunities. Should American companies choose to diversify their supply chains to avoid the tariffs, it could lead to long-term challenges for the Indian textile market as buyers may permanently shift their preferences.
Response from Indian Seafood Farmers
Amidst the sweeping changes due to increased tariffs, Indian seafood farmers are facing tough decisions about their futures. Many shrimp farmers, especially in states like Andhra Pradesh, have begun reporting decreased sales as the American market reacts to price increases. With shrimp exports being a major revenue source, this tariff hike effectively places a stranglehold on livelihoods, driving some farmers to consider scaling back operations or seeking alternative markets amid declining demand.
In response to these tariff measures, farmers and exporters alike are attempting to pivot by developing new trade relationships with neighboring countries. However, such adjustments take time and resources, leading to further financial strain on already struggling farmers. This chain reaction of lost revenue and market instability not only affects Indian businesses but also US consumers who may pay more for imported seafood and could face shortages of popular products.
Consumer Reaction to Rising Prices
As the full effects of the tariffs on Indian imports kick in, American consumers are left grappling with rising prices. For many families, the cost of clothing, seafood, and other products will directly be affected by this trade policy shift. Retailers may struggle to maintain competitive pricing, prompting them to pass along costs to the consumer. This situation elaborates how intricate and far-reaching the ramifications of such tariffs can be—showing that a political decision can reverberate through the economy and alter households’ spending habits.
Additionally, consumer reactions to price increases vary widely. Some may actively seek out alternative products, while others are left with no choice but to absorb the higher costs. The importance of sourcing trends shifts as U.S. companies adapt to changing prices and trade routes. As a result, the consumer landscape may evolve, with new preferences emerging as individuals seek to avoid inflated prices while still meeting their household needs.
Geopolitical Implications of Tariffs
The imposition of tariffs on Indian imports reflects broader geopolitical strategies being employed by the Trump administration. Especially in light of India’s recent dealings in Russian oil, these tariffs serve not only to adjust economic dynamics but also to promote U.S. foreign policy interests. The overall picture underscores how international trade is intertwined with political maneuvering—a stark reminder of the delicate balance countries must navigate between economic cooperation and political posturing.
Over time, the repercussions of these tariffs can redefine alliances and compel countries to reassess their trade relationships. As India adjusts to the new economic landscape, there may be calls for re-evaluating trade policies and engaging in diplomatic dialogues to address these issues, aiming to avert future economic sanctions. The potential for deeper economic ties depends heavily on how well nations can negotiate their interests amid changing global dynamics.
The Future of Indian Exports
The forecasts predict that Indian exports will experience a significant downturn due to the tariffs, with estimates dropping to around $50 billion by fiscal year 2026. This decline poses not only immediate economic challenges for exporters but also longer-term structural questions regarding India’s position in global trade. If consumer dependence on Indian-produced goods falls, it may lead to a permanent reduction in market share, severely altering the export landscape.
In adapting to these challenges, strategies such as diversification of export products and strengthening ties with new trading partners must be explored. As retailers and suppliers reconsider their sourcing options, timely action and negotiation could help mitigate the impact of U.S. tariffs. However, failure to adapt could lead to a diminishing role for India in the international market, affecting both producers and consumers across borders.
Notable Exceptions to Tariffs
Amidst the imposing tariffs on most Indian imports, there are notable exceptions—particularly in the pharmaceutical sector. With a heavily established reliance on India for generic drugs and medicines, the U.S. has carved out exemptions that maintain the flow of essential healthcare products. This aspect shows that while trade policy aims to implement tariffs for strategic reasons, public health considerations can trigger a more nuanced approach.
Additionally, exemptions for semiconductors and electronics further highlight the complexities of trade relations between the U.S. and India. Despite the overarching hostile tariff environment, sectors that support technological advancement remain crucial. Allowing these exceptions suggests a strategic effort to diversify trade partnerships while balancing economic pressure on less critical products. Analyzing which sectors receive exemptions could unravel insights on future U.S. trade policy direction.
Long Term Perspectives on US Trade Policy
The long-term implications of tariffs on Indian imports will inevitably shape the trajectory of U.S. trade policy. While many stakeholders may breathe a sigh of relief regarding exemptions in key industries, the overarching atmosphere of uncertainty may promote a culture of cautious trading behavior. American consumers will encounter a landscape defined by volatility, potentially limiting their purchasing power and available choices in the international marketplace.
Moreover, as geopolitical tensions ebb and flow, it will be essential for U.S. policymakers to balance economic interests with broader diplomatic goals. A more cohesive trade policy could lead to more predictable outcomes for both American consumers and Indian exporters. Ultimately, the evolution of U.S. trade policy will need to consider the interconnected relationships forged through imports, exports, and mutual reliance in a complex global economy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the implications of the US tariffs on Indian imports for American consumers?
The US tariffs on Indian imports, particularly the doubling of tariffs to 50%, are expected to result in higher prices for American consumers. Key sectors affected include textiles and seafood, which could see significant price hikes due to reduced supply from India. This increase in costs can lead to surging consumer prices for clothing, shrimp, and other goods traditionally sourced from India.
How might Trump tariffs on India impact Indian seafood exports?
Trump’s tariffs on India, especially the high rates imposed on seafood like shrimp, are likely to drastically reduce Indian seafood exports to the US. As Indian suppliers struggle to compete with alternative sourcing from nations like Ecuador and Vietnam, the overall export value could decline to under $50 billion in the near future.
What effect do these tariffs have on textiles from India?
Textiles from India are significantly impacted by the US tariffs, with American businesses potentially seeking alternatives from countries with lower production costs, such as Vietnam and Bangladesh. This shift may lead to increased clothing prices for US consumers as American brands adjust their sourcing strategies.
Can you explain the impact of US trade policy on Indian exports?
US trade policy, particularly the recent tariffs imposed by Trump, poses a significant threat to Indian exports, especially in sectors like textiles and seafood. As tariffs rise, Indian exporters may see their market share diminish, thus impacting their profitability and labor opportunities at home.
What are the key concerns for American consumers regarding increased tariffs on Indian imports?
American consumers are primarily concerned about rising prices stemming from increased tariffs on Indian imports. The sectors most affected include textiles, seafood, and luxury goods like jewelry, which could lead to a broader increase in costs for goods in retail markets.
How do the tariffs impact the Indian jewelry industry?
The tariffs imposed on Indian imports threaten the jewelry industry in India, where a significant number of workers rely on exports to the US. These heightened tariffs can reduce profit margins and potentially disrupt the supply chain, making it difficult for Indian jewelers to compete.
Are there any exemptions from the US tariffs on Indian imports?
Yes, there are notable exemptions from the US tariffs on Indian imports, particularly for the pharmaceutical industry and certain electronics like smartphones. While some products face steep tariffs, the exemptions could help maintain competitive pricing for crucial imports.
What alternatives are US companies considering due to the tariffs on Indian goods?
US companies are exploring alternative sourcing options from countries such as Pakistan for basmati rice, and Vietnam and Bangladesh for textiles and spices. This shift may alleviate some immediate supply chain issues but could also lead to increased prices for consumers.
How are Indian shrimp farmers affected by the US tariffs?
Indian shrimp farmers face significant challenges due to the US tariffs, which increase competition from alternative suppliers. The initial and now doubled tariff rate puts Indian shrimp at a disadvantage in the American market, threatening the livelihoods of many farmers and impacting overall export volumes.
What is the long-term outlook for US tariffs on Indian imports?
The long-term outlook for US tariffs on Indian imports remains uncertain. While current policies threaten various sectors, geopolitical factors and trade negotiations could lead to modifications or easing of these tariffs, potentially restoring trade balance and pricing for both American and Indian markets.
| Key Area | Impact | Future Outlook |
|---|---|---|
| Import Tariffs | Tariffs on Indian imports doubled to 50%, significantly affecting prices for consumers. | Imports from India expected to decrease to under $50 billion by 2026. |
| Seafood & Food Items | Shrimp and spices industries particularly affected, leading to possible price hikes. | U.S. sourcing from alternative markets like Ecuador, Pakistan, and Vietnam. |
| Textiles & Apparel | Price increases expected; domestic labor and production opportunities in India may decline. | Shifts to alternative suppliers in countries like Vietnam, Bangladesh, and Belgium. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Exempt from the new tariffs, but the future of any tariffs remains uncertain. | Trump has indicated potential future tariffs on pharmaceuticals, affecting pricing. |
Summary
US tariffs on Indian imports have escalated to 50%, resulting in significant repercussions for American consumers and various industries. The doubling of these tariffs will likely increase prices on key goods such as textiles, seafood, and electronics, steering American businesses towards alternative markets. As companies navigate the changes and seek new suppliers, American consumers may see a shift in product availability and pricing, reinforcing the dynamic relationships between US tariffs and Indian exports.