Rare earth elements are vital components in today’s technology-driven world, playing an essential role in the production of smartphones, electric vehicles, and various military equipment. The recent geopolitical landscape, heavily influenced by China export restrictions, has drawn attention to the fragility of the US rare earth supply chain. As tensions rise, particularly in light of Trump’s tariffs, the importance of securing a stable supply of these rare earth materials cannot be overstated. With China dominating global production, the U.S. faces significant challenges in rare earth mining and sourcing alternatives. This delicate situation underscores the need for immediate steps to strengthen domestic capabilities in the face of potential supply disruptions.
As we delve into the significance of rare earths, it’s essential to recognize them by their various alternative names, including critical minerals and strategic materials. Often hidden in the broader discussions about technology and manufacturing, these elements are integral to ensuring the functionality of modern devices. In light of recent developments regarding China’s tightening grip on exports, it becomes clear that the stakes of securing these vital resources are higher than ever. The implications of a stronghold on critical minerals extend beyond national security, affecting sectors from consumer electronics to renewable energy. By understanding the pressing need to establish a resilient supply chain for these indispensable materials, we can appreciate their overarching importance in global trade and innovation.
The Critical Role of Rare Earth Elements in Modern Technology
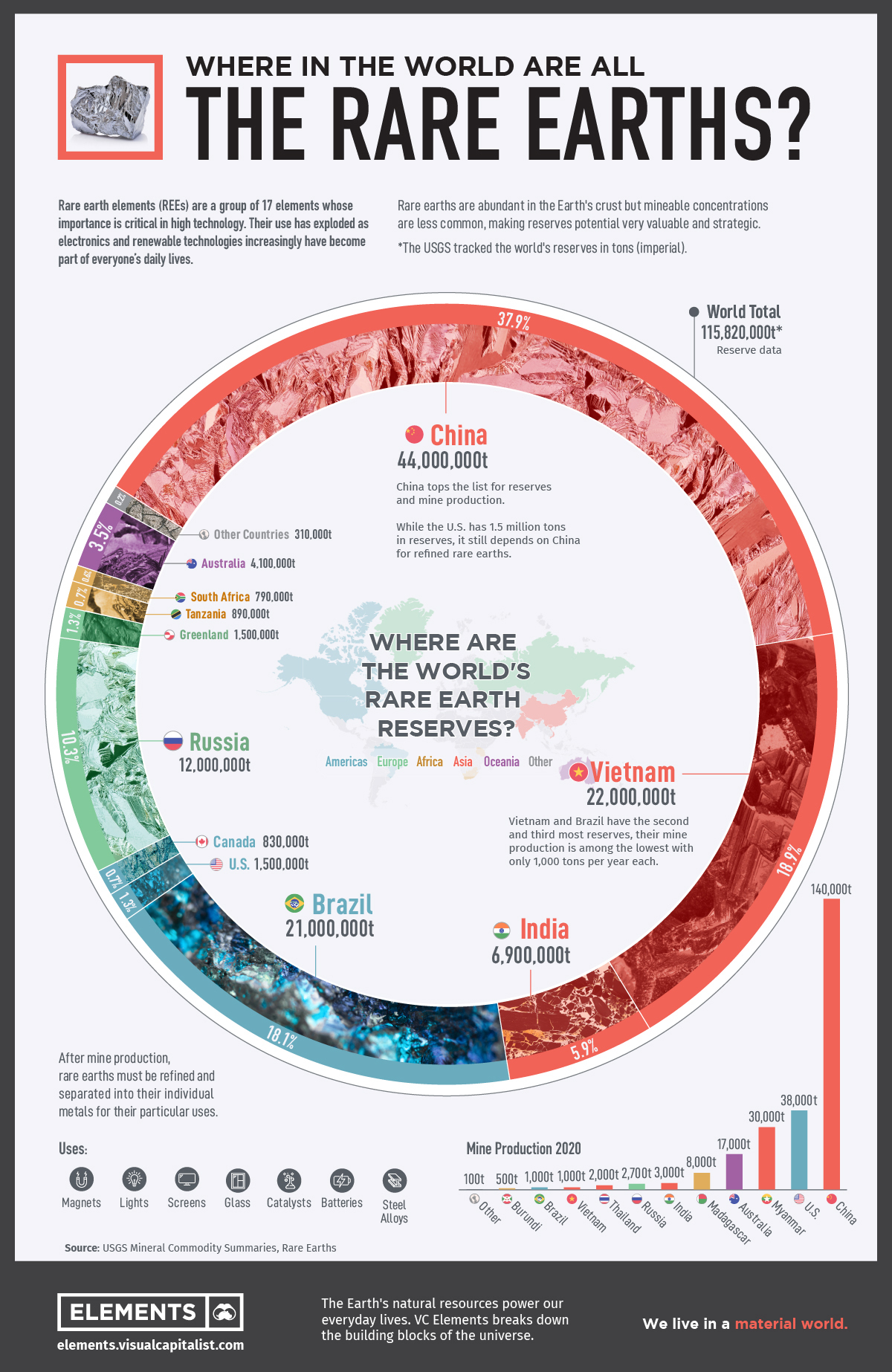
Rare earth elements (REEs) represent a group of 17 chemically similar metals essential for many modern technologies. These elements are used in a variety of applications, from high-performance magnets crucial for electric vehicles to phosphors in LED lights and catalysts for petroleum refining. As technology continues to develop at a rapid pace, the demand for these rare earth materials grows exponentially, highlighting their indispensable role in the manufacturing of smartphones, electric vehicles, and renewable energy technologies.
China currently dominates the global rare earth supply chain, producing over 60% of the world’s REEs. This monopoly has raised concerns in the U.S., especially in light of the trade conflicts with China. With increasing tensions, the U.S. must recognize the importance of securing a stable and independent supply of rare earth materials to maintain its technological and military capabilities. Exploring domestic mining opportunities and investing in processing facilities are crucial steps to reducing dependency on Chinese exports.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are rare earth elements and why are they important for the US rare earth supply chain?
Rare earth elements (REEs) are a group of 17 metals critical for modern technology, including electronics, aerospace, and defense systems. The US rare earth supply chain heavily depends on these materials for producing advanced technologies like computer chips, electric vehicles, and military hardware. Their importance has surged due to growing demand in various industries, making secure access to these elements vital for national security and economic stability.
How do China export restrictions impact rare earth materials availability for the US?
China’s export restrictions on rare earth materials significantly threaten the availability of these essential elements for the US. As China produces about 85% of the world’s rare earths, any restriction can disrupt supply chains for many American industries, from electronics to defense, underscoring the urgent need for the US to develop its own sources and infrastructure for mining and processing rare earths.
What is the impact of Trump tariffs on the rare earth supply chain?
Trump’s tariffs have complicated the US rare earth supply chain by increasing production costs for domestic companies reliant on imported materials. These tariffs can hinder investments in new mining and processing facilities within the US, which are crucial for reducing dependency on Chinese rare earths. Consequently, they may incentivize American companies to seek alternative sources and innovate in local production.
Why is rare earth mining significant in the context of US-China trade relations?
Rare earth mining has become a focal point in US-China trade relations due to its strategic importance. As the US seeks to reduce reliance on China’s rare earths amidst escalating trade tensions, the ability to mine and process these critical materials domestically is seen as essential for national security and maintaining technological independence. This mining capability is vital for supporting various industries, including defense and technology.
What challenges does the US face in developing its own rare earth elements capacity?
The US faces significant challenges in developing its own rare earth elements capacity, including a lack of infrastructure, dwindling expertise in mining and processing, and regulatory hurdles. Establishing a fully operational domestic supply chain may take years, as experts predict it could be eight to ten years before significant new production capabilities arise, emphasizing the urgency of overcoming these barriers.
How do geopolitical factors influence rare earth materials and trade?
Geopolitical factors significantly influence rare earth materials and trade, particularly in the context of US-China relations. China’s control over a large portion of the global rare earth supply allows it to leverage these resources in trade negotiations. Export controls, tariffs, and bilateral tensions can impact the availability of these materials, making them critical in geopolitical strategies and international relations.
What are potential alternatives to reliance on China for rare earth supply?
Potential alternatives to reliance on China for rare earth supply include developing new mining projects in countries like Australia and Canada, investing in domestic mining and processing facilities, and exploring unconventional sources such as ocean floor deposits. Additionally, advancements in recycling technologies for rare earth elements from used electronics can contribute to a more sustainable and independent supply chain.
What can the US do to secure its rare earth supply chain amidst rising tensions with China?
To secure its rare earth supply chain amidst rising tensions with China, the US can invest in domestic mining and processing capabilities, promote research into alternative sourcing, and encourage partnerships with allied countries. Policies supporting innovation and investment in critical minerals will help diversify the supply chain and reduce the nation’s dependence on Chinese rare earth materials.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Impact of Tariffs | China has implemented export restrictions on rare earth elements in retaliation to Donald Trump’s tariffs. |
| Importance in Technology | Rare earth elements are essential for producing weapons, computer chips, and electric vehicles. |
| China’s Dominance | China produces the majority of rare earth elements and has built extensive processing infrastructure over decades. |
| U.S. Dependency | The U.S. is years away from establishing its own supply chain for rare earths, impacting national security and technology sectors. |
| Potential Consequences | Further restrictions from China could severely affect U.S. industries, especially defense and technology. |
| Future Prospects | U.S. initiatives to reduce dependency include exploring mining options domestically and even on the Moon. |
Summary
Rare earth elements are crucial components in modern technology and defense systems, highlighted by the ongoing tensions between the U.S. and China over trade tariffs. The geopolitical landscape surrounding these materials underscores their significance as both a strategic and economic resource. As the U.S. seeks to diminish its reliance on Chinese supplies, the road ahead will involve navigating complex trade relationships, investing in domestic capabilities, and establishing sustainable supply chains for rare earth elements.