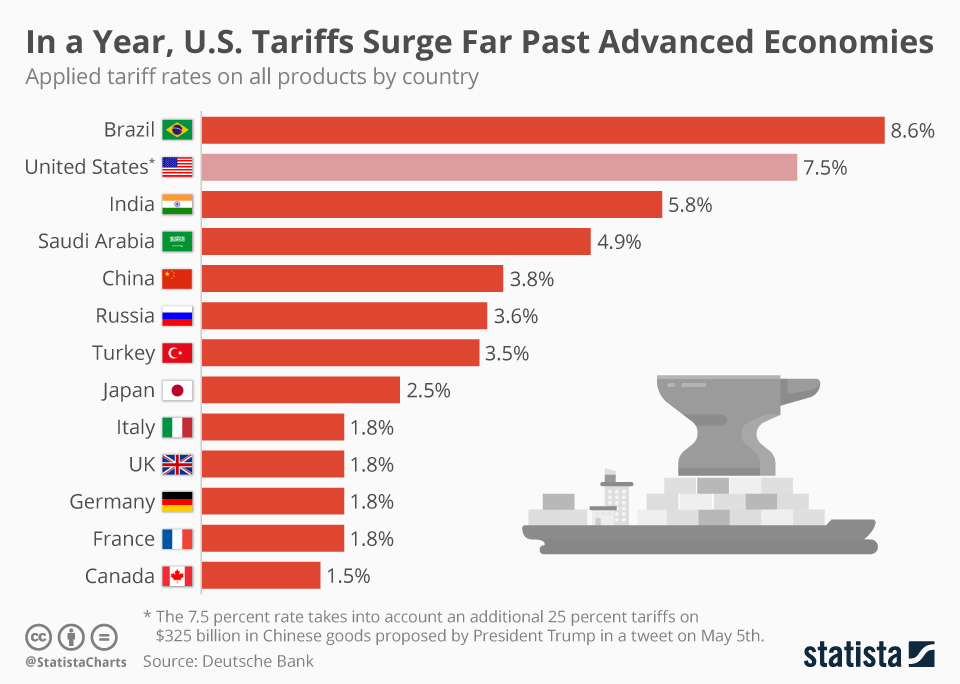
U.S. Tariffs have become a hot-button issue in international trade discussions, especially under the administration of President Donald Trump. The proposed tariffs, often referred to as Trump’s tariffs, aim to impose taxes on a range of imported goods in an effort to bolster domestic manufacturing and create jobs. However, the impact of tariffs can trickle down to consumers, escalating prices and straining household budgets. As reciprocal tariffs are introduced, they could spark a significant backlash from trading partners, leading to a potential economic slowdown. Understanding the nature and consequences of these tariffs is crucial as they play a pivotal role in shaping the current trade policy landscape.
The recent wave of imposed duties, commonly dubbed import tariffs, signifies a pivotal shift in the U.S. approach to global trade. Under Trump’s administration, these taxes are designed as a countermeasure to what is perceived as unfair practices by other nations, aiming to level the playing field. However, this protective measure raises concerns about the ramifications on both consumers and businesses. The reciprocal nature of these tariffs could incite a series of retaliatory actions from trade partners, further complicating diplomatic relations. Analysts are warning that such trade barriers may not only inflate prices but also hinder economic growth.
Understanding U.S. Tariffs and Their Implications
U.S. tariffs, often referred to as taxes on imported goods, play a critical role in shaping domestic and international trade relationships. Recently, President Trump’s administration has proposed a comprehensive set of reciprocal tariffs aimed at equalizing export tax levels. These tariffs are designed to bolster the American workforce by encouraging companies to invest domestically. However, critics argue that such policies may lead to increased prices for consumers and put a strain on international relationships. As outlined in various economic analyses, the impact of these tariffs can ripple through various sectors, affecting not only the prices of goods but also the overall economy.
It’s important to note that while tariffs are touted as a means to protect American jobs, they could inadvertently lead to a contraction in consumer spending. As prices of goods inevitably rise due to added tariffs, low- and middle-income families could find themselves facing financial strain. Economists predict an increase in the coast of essentials, from electronics to clothing, which only exacerbates existing economic disparities. Without careful consideration and strategic trade policies, the intended benefits of tariffs could quickly diminish, leading to a less favorable economic landscape.
The Impact of Trump’s Trade Policy on American Consumers
President Trump’s trade policies, frequently criticized for their potential to ignite a trade war, are set against a backdrop of economic uncertainty. While authoritarian trade practices suggest a means to ensure fairness in American industry, many argue that higher tariffs could simply lead to rising prices for consumers. For instance, the anticipated 10% increase in the cost of electronics could deter consumer spending, which is vital for sustaining economic growth. In addition, even essential goods like food are likely to see price hikes as import costs rise, putting more pressure on American households.
Moreover, the strain on consumer wallets could lead to a slowdown in economic activity. The overarching goal of boosting domestic jobs through tariffs may inadvertently hinder consumer confidence, driving people to spend less rather than more. This decline in spending could stifle business investments and ultimately lead to job losses. Thus, while the intended message of President Trump’s trade policy is focused on protecting the American worker, the collateral damage could raise questions about the viability of such an approach in promoting sustainable economic health.
Reciprocal Tariffs: A Double-Edged Sword
Reciprocal tariffs are designed to create a level playing field in international trade; however, they can act as a double-edged sword. On one hand, these tariffs may incentivize countries to enter renegotiations for fairer trade practices, benefiting U.S. manufacturers. On the other hand, the imposition of reciprocal tariffs can escalate tensions, leading to retaliatory trade measures from affected nations. For instance, the Chinese government has already responded to U.S. tariffs with its own tariffs on American agricultural products, creating a cycle of economic conflict that jeopardizes the livelihoods of American farmers.
The economic ripple effects of reciprocal tariffs also extend to everyday consumers. As international relationships sour and trade barriers rise, consumers may face scarcity of certain goods, alongside rising prices as companies pass on their increased costs. The predicted impact on cost-of-living is especially significant as essential items, from avocados to electronics, may see sharp increases—up to 6% or more. Therefore, while reciprocal tariffs aim to protect American interests, they could equally impact domestic prices and consumer choices.
Navigating Economic Slowdown Amidst Tariff Policy Changes
The reality of an economic slowdown amidst changing tariff policies has raised concerns among economists and consumers alike. As businesses grapple with uncertainty, many are opting to cut back on investments and hiring—which can further exacerbate the slowdown. Kalemli-Özcan’s assessments highlight that the unpredictability surrounding tariffs makes planning for the future difficult for both companies and consumers. As the specter of recession looms, consumer confidence wanes, which stifles growth across various sectors.
From a macroeconomic standpoint, a slowdown can have various adverse effects. When spending declines and businesses deem the future too uncertain, the virtuous cycle of growth can quickly turn sour. Economic stability, driven by consumer confidence and spending, is paramount for job creation and industry growth. However, unanswered questions regarding tariffs and trade relationships may prompt consumers to tighten their belts, ultimately leading to reduced economic activity. This situation indicates that while tariffs may be a tool for addressing trade disparities, they could also inadvertently usher in an era of economic challenges.
The Role of China in U.S. Tariff Discussions
China’s role in the tariff discussions has been a focal point of President Trump’s trade strategy. With the world’s largest economy, China’s response to U.S. tariffs carries significant weight. Recent escalations, including increased tariffs on American agricultural exports, have prompted concerns regarding the sustainability of U.S. farmers dependent on Chinese markets. The interconnectedness of these two economies means that trade policies will not only impact pricing but also influence the broader economic landscape and bilateral relations.
Moreover, Trump’s threats to impose even higher tariffs have sparked a wave of apprehension about potential supply chain disruptions. As companies rely on Chinese imports for key raw materials and goods, sudden changes could lead to operational challenges and delivery delays. This dualistic relationship necessitates careful negotiation to avoid detrimental impacts on both economies. The implications of these tariff policies extend far beyond trade numbers, affecting real lives and livelihoods on both sides of the Pacific.
Understanding Tariffs: The Rise and Fall of U.S. Trade Relations
The history of tariffs reveals a complex interplay of protectionism and global trade dynamics. As America asserts its trade policies under the Trump administration, the long-standing principles of free trade are being challenged. Tariffs are often seen as a necessary measure to address trade injustices, but at what cost? Historically, the U.S. has benefited from free trade agreements that have fostered interdependence and growth; however, the current wave of tariffs risks isolating America from advantageous trade partnerships.
As the nature of global commerce evolves, any shifts towards protectionism could prove detrimental in the long run. The cost of materials may rise, manufacturing could become less competitive, and consumers may experience higher prices across the board. Thus, understanding the multiple dimensions of tariffs—both positives and negatives—is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of the current U.S. trade policy. Policymakers must weigh the benefits of protection against the potential fallout from distancing America from key trade partners.
The Long-Term Effects of Tariff Implementation
The long-term effects of implementing tariffs could reshape the landscape of American trade and industry for years to come. As immediate reactions to tariffs often favor domestic production, the longer-term implications might include diminished access to global markets and innovations that stem from international collaborations. When companies become less competitive due to increased costs, the downstream effects can stifle growth and technological progress essential for survival in a highly competitive global market.
Experts posit that the impact of tariffs will likely cascade across industries, leading to a shift in where companies choose to invest. Over time, if the protectionist policies persist, the cumulative effect could result in a decline in economic vitality while fostering an environment of isolationism. The dual-pressure of rising costs along with limited global partnerships could result in a fragmented economy, further exacerbating challenges faced by consumers and businesses alike.
Consumer Behavior Shifts in Response to Tariff Changes
Consumer behavior is likely to shift dramatically in response to the changing landscape of tariffs and trade policies. As prices rise due to tariffs on imports, consumers may begin to reassess their purchasing habits, leaning towards less expensive alternatives or delaying purchases altogether. This adaptive strategy is observed during times of economic uncertainty, where consumers prioritize essential spending while being more careful with discretionary expenses. The immediate fear of rising prices could deter consumers from engaging in spending, leading to a significant dip in overall economic activity.
Moreover, shifting consumer preferences can prompt businesses to pivot their strategies to maintain sales and market share. Companies may look to source materials domestically or from other countries not subject to the same tariffs. Ultimately, the heightened sensitivity in consumer behavior will not only impact individual businesses but could change the dynamics of entire industries, as businesses scramble to adapt, potentially leading to new trends in manufacturing and sourcing.
The Broader Economic Impact: Jobs and Industry
The broader economic impact of tariffs can be profound, influencing jobs and industry across the United States. While the administration’s rhetoric claims that tariffs will create jobs domestically, the reality may tell a different story. As firms face rising costs, they may decide to automate or outsource certain operations to maintain profitability, leading to job cuts instead of growth. This paradox within tariff policy raises critical questions about whether short-term gains in certain sectors can outweigh long-term job losses across the economy.
Furthermore, industries like agriculture that heavily rely on exports could find themselves facing significant challenges as retaliatory tariffs bite deeper. With a growing reliance on international markets, any downturn in exports can contribute to job losses and economic instability. Therefore, the interconnected nature of tariffs and job creation demands careful consideration, balancing protectionist measures with initiatives that truly foster long-term employment and economic resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the potential impacts of U.S. tariffs on American consumers?
U.S. tariffs, particularly those implemented under Trump’s trade policy, are likely to increase the prices of imported goods. For instance, consumers may see a 10% price hike on electronics and a 2.9% increase on fresh produce due to reciprocal tariffs. Low- and middle-income families will disproportionately bear the burden of these costs, as they may not have the financial means to absorb higher prices.
How do Trump tariffs affect international trade relations?
Trump’s tariffs may strain international trade relations as they are seen as punitive measures against trading partners like China, Mexico, and Canada. These reciprocal tariffs could provoke retaliatory measures, impacting U.S. exports and leading to a trade war that may isolate American companies from global markets and innovations.
What are reciprocal tariffs and how do they relate to U.S. trade policy?
Reciprocal tariffs are taxes imposed on imports that match the tax rates on U.S. exports. Under Trump’s trade policy, these tariffs aim to level the playing field for American businesses. However, they can lead to higher consumer prices and disrupted supply chains, potentially resulting in economic slowdowns.
Is there evidence that tariffs can lead to an economic slowdown in the U.S.?
Yes, experts suggest that the implementation of U.S. tariffs, particularly under the current administration, might contribute to an economic slowdown. Increased costs for companies can lead to lower consumer spending and reduced business investment, causing a slowdown in overall economic growth.
How might U.S. tariffs affect the prices of goods imported from China?
U.S. tariffs on Chinese goods, having increased to 20% and potentially more, are expected to raise the prices of essential products, including electronics and household items. This increase in costs is likely to be passed on to consumers, making everyday goods more expensive.
What is the relationship between U.S. tariffs and the trade deficit?
While the Trump administration suggests that tariffs will reduce the trade deficit by encouraging domestic production, experts argue that tariffs alone cannot solve this issue. By isolating U.S. companies from international markets, tariffs may hinder innovation and competitiveness, ultimately affecting the trade deficit negatively.
What are the consequences of tariffs on agriculture and U.S. farmers?
The imposition of tariffs by countries like China on U.S. agricultural products, such as a 15% tax on chicken and wheat, threatens the livelihoods of American farmers. With China potentially seeking alternatives from other countries, U.S. farmers may face significant market losses and reduced sales.
How can unpredictable U.S. tariff policies impact consumer behavior?
Uncertain U.S. tariff policies may discourage consumer spending as people anticipate rising prices and potential shortages. Businesses may also delay investments or hiring due to uncertain future costs, contributing to a sluggish economy that affects overall market confidence.
What strategic actions did Trump mention regarding tariffs on China?
President Trump indicated the possibility of reducing tariffs on China as part of negotiations, particularly concerning the sale of TikTok. This suggests that tariffs can be used as a bargaining tool to achieve other economic or strategic objectives, impacting the overall trade relationship.
Are tariffs likely to increase the competitiveness of U.S. industries?
While tariffs are intended to enhance domestic competitiveness by protecting U.S. industries, experts warn that they may also isolate companies from global innovations. Without complementary policies to foster domestic manufacturing, tariffs could hinder rather than help U.S. industry competitiveness.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Announcement of Tariffs | President Trump’s ‘Liberation Day’ on April 2 will announce reciprocal tariffs on imported goods. |
| Impact on Consumers | Tariffs will likely increase prices of electronics and other goods, disproportionally affecting low- and middle-income families. |
| Trade Relations | Experts warn that tariffs could lead to strained trade relationships, with potential global trade war repercussions. |
| Domestic Manufacturing Challenges | Experts believe tariffs alone won’t solve the trade deficit; significant time is required to scale up domestic industries. |
| Retaliation from China | China has retaliated with tariffs on U.S. agricultural products, affecting American farmers. |
| Effect on North American Trade Partners | Mexico and Canada will face 25% tariffs on goods, with food prices expected to rise significantly. |
| Economic Outlook | Tariffs may slow economic growth and reduce consumer spending, leading to a potential recession. |
Summary
U.S. TARIFFS are poised to create significant economic upheaval as President Trump’s administration considers reciprocal levies on imported goods. This strategy aims to protect American jobs but risks increased consumer costs and strained international trade relations. Experts warn that such measures may not only isolate the U.S. from global markets but also hurt domestic consumers, especially those in lower income brackets. As the backdrop of a possible global trade war looms, the long-term implications of these tariffs could lead to reduced access to foreign innovations and a slowdown in American economic growth.