Pregnancy-related deaths have become an alarming concern in the United States, showing a staggering increase of nearly 28% between 2018 and 2022. A study published in JAMA Network Open reveals critical insights into this issue, highlighting the increasing maternal mortality rate, particularly among marginalized communities. The research points to a significant peak in pregnancy-related deaths in 2021, likely exacerbated by the COVID-19 impact on maternal health. Racial disparities in pregnancy outcomes are troubling, with American Indian and Black women facing the highest risks, leading to calls for improving maternal health outcomes through better access to postnatal care. As we delve into these findings, it becomes clear that addressing this crisis requires urgent action across the healthcare system to protect both mothers and babies alike.
The tragic phenomenon of maternal fatalities during pregnancy and shortly after childbirth highlights an urgent public health crisis. Known as maternal mortality, these incidents draw attention to the inequalities present in our healthcare system, especially regarding care access for diverse racial and ethnic groups. Recent studies show an increase in such fatalities, underscoring a pervasive need to address both systemic barriers and social determinants that significantly influence maternal health. This discussion emphasizes the importance of equitable postnatal care access, aiming to enhance outcomes for all expectant mothers, regardless of their background. Tackling this pressing issue must involve comprehensive strategies to reduce racial and ethnic disparities in pregnancy and ensure healthier futures for mothers and their infants.
The Alarming Increase in Pregnancy-Related Deaths
Recent findings indicate a distressing surge in pregnancy-related deaths in the United States, with an increase of nearly 28% from 2018 to 2022. This troubling trend was highlighted in a study published in JAMA Network Open, which utilized data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The analysis revealed that the pregnancy-related mortality rate escalated from 25.3 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2018 to a peak of 44.1 in 2021. Although there was a slight decline to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 in 2022, the overall upward trajectory raises significant concerns regarding maternal health outcomes across demographic lines and geographical locations.
The implications of this increased mortality rate suggest systemic issues that must be addressed urgently. Various factors contribute to the rising maternal mortality rate, including disparities in healthcare access and quality, particularly for minority populations. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women face the highest rates of pregnancy-related deaths, emphasizing the intersection of racial disparities with maternal health issues. Continued research and policy advocacy are necessary to understand the underlying causes of these disparities and to implement effective interventions that could enhance maternal health outcomes.
COVID-19 and Its Impact on Maternal Health
The COVID-19 pandemic has undoubtedly had a profound effect on health systems globally, and the observations from the recent study suggest that it may have exacerbated existing challenges in maternal health. As Dr. Rose Molina mentioned, the pandemic’s impact on healthcare delivery could have influenced the troubling rise in pregnancy-related deaths observed in 2021. Factors such as healthcare disruptions, increased stress on healthcare professionals, and barriers to accessing necessary maternal care services during the pandemic likely played significant roles in these outcomes.
Moreover, the pandemic underscored the vulnerabilities within the maternal health framework, particularly for marginalized communities. Enhanced social determinants of health during the public health crisis have illuminated the dire need to reinforce the infrastructure supporting pregnancy care. Addressing COVID-19’s impact on maternal health will require concerted efforts to rethink and reform healthcare delivery systems to ensure equitable access to care, particularly for high-risk populations.
Racial Disparities in Pregnancy-Related Mortality Rates
Racial disparities in pregnancy-related mortality rates reveal alarming inequalities in maternal health, emphasizing the need for targeted interventions. The study highlights that American Indian and Alaska Native women experience pregnancy-related deaths at rates 3.8 times higher than white women, while non-Hispanic Black women encounter rates 2.8 times higher. These stark differences point towards systemic issues within the healthcare system, including access to quality prenatal and postnatal care, which are critical for improving maternal health outcomes.
To address these disparities effectively, it is crucial to acknowledge the intersection of socioeconomic factors and healthcare access. Income differences, geographic barriers, and healthcare biases contribute significantly to these variations in mortality rates. By implementing policies that ensure equitable access to comprehensive maternal healthcare services across all racial and ethnic groups, we can work towards reducing the gap in pregnancy-related mortality rates and advocating for improved maternal health outcomes for all.
The Importance of Postnatal Care in Maternal Health
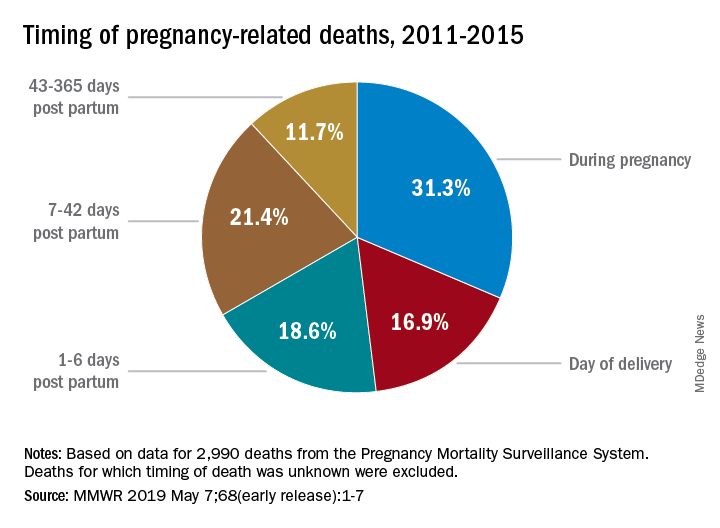
Postnatal care is a vital component of maternal health that significantly impacts long-term health outcomes. The recent study’s findings suggest a gap in continuity of care that affects mothers after childbirth, particularly in relation to late maternal deaths that occur between one month to a year after delivery. American Indian and Alaska Native women, who have the highest rates of late maternal deaths, may face challenges accessing essential postnatal services, which are crucial for monitoring and addressing potential health issues that can arise after pregnancy.
Improving access to postnatal care can help reduce the rates of late maternal deaths and enhance overall maternal health outcomes. Healthcare systems must prioritize and expand postpartum services to ensure that all mothers receive the necessary support and care during the critical period following childbirth. Implementing policies that promote comprehensive postnatal care can lead to better health outcomes for mothers and their infants.
Enhancing Access to Prenatal Care Among Vulnerable Populations
Access to quality prenatal care is foundational to reducing pregnancy-related deaths, particularly among vulnerable populations. The study indicates that significant variations exist in state-level access to prenatal services, with disparities often based on race, ethnicity, and socio-economic status. Expanding Medicaid coverage and implementing programs that provide resources for pregnant individuals in underserved areas are essential steps towards improving access to prenatal care.
By ensuring that all pregnant women have access to necessary prenatal screenings and regular check-ups, healthcare providers can identify and address potential complications early in the pregnancy. This proactivity is key to minimizing the risks associated with pregnancy and ultimately reducing the maternal mortality rate across different demographics. Communities that engage in proactive prenatal care initiatives will pave the way towards healthier pregnancies and improved maternal health outcomes.
Cardiovascular Health and Pregnancy Outcomes
Cardiovascular disease has been identified as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the United States. This alarming statistic highlights the need for healthcare providers to monitor maternal heart health closely before, during, and after pregnancy. Women with pre-existing conditions or risk factors must receive targeted interventions to manage their cardiovascular health, thus potentially decreasing the likelihood of related pregnancy complications.
Furthermore, educating mothers on the importance of cardiovascular health can empower them to seek timely medical attention for any concerning symptoms during pregnancy. Recognizing the connection between heart health and pregnancy outcomes is essential to improving maternal health care practices. By fostering an integrated approach that addresses both cardiovascular and maternal health, healthcare systems can contribute to lower rates of maternal mortality.
Investing in Maternal Health Infrastructure
The findings of the study emphasize a critical need for continued investment in maternal health infrastructure. Establishing robust systems that focus on prenatal, perinatal, and postnatal care can directly impact the rates of pregnancy-related deaths. Policymakers must prioritize funding for maternal health programs, especially for those serving marginalized communities, to ensure the availability of comprehensive resources and support throughout the pregnancy journey.
These investments are vital for reducing the disparities observed in maternal mortality across different racial and ethnic groups. By allocating resources towards enhancing healthcare programs and reducing barriers that impede access to care, there is great potential to improve overall maternal health outcomes. A concerted effort to strengthen maternal health infrastructure is crucial for creating an equitable and effective healthcare landscape.
The Role of Community Support in Maternal Health
Community support plays a pivotal role in improving maternal health outcomes, particularly among marginalized populations. Support networks can provide essential resources, guidance, and access to healthcare services that pregnant individuals may lack. Engaging local organizations and community leaders in maternal health initiatives can help bridge gaps in care while fostering an environment of solidarity and encouragement for expectant mothers.
Additionally, community-driven programs that promote education around pregnancy health and wellness can empower individuals to take charge of their pregnancies. Access to prenatal classes, nutrition resources, and mental health support groups can significantly enhance the experience of pregnancy, contributing to better health outcomes for both mothers and their babies. Emphasizing community involvement in maternal health illustrates the collective effort needed to address disparities and reduce pregnancy-related mortality.
Future Directions for Maternal Health Research
Future research in maternal health is imperative to address the multifaceted challenges evident in the rising pregnancy-related deaths. Understanding the complexities behind these statistics is essential for effective policy-making and intervention development. Researchers must dive deeper into the social, economic, and healthcare-related factors contributing to maternal mortality rates, particularly focusing on how systemic inequalities affect different demographic groups.
Furthermore, long-term studies that track maternal health outcomes post-pregnancy could provide invaluable insight into latent health implications resulting from pregnancy and childbirth. This knowledge will inform the healthcare system in tailoring services to meet the unique needs of mothers, ensuring that care extends beyond the birth of a child. By fostering a research environment that prioritizes maternal health, we can work towards meaningful improvements and a reduction in pregnancy-related deaths.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors contribute to the increase in pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
Recent studies indicate that disparities in access to care, particularly prenatal, labor, delivery, and postnatal services, contribute significantly to the rise in pregnancy-related deaths. Additionally, socioeconomic and systemic biases in the healthcare system exacerbate these issues, particularly among racial and ethnic minorities.
How has COVID-19 impacted maternal health and pregnancy-related deaths?
The COVID-19 pandemic has been suggested as a factor influencing maternal health outcomes, possibly leading to higher pregnancy-related deaths due to disruptions in healthcare access and increased stress on the healthcare system, particularly noted during the peak of the pandemic in 2021.
What is the maternal mortality rate in the U.S., and how does it vary by state and race?
The U.S. has experienced a significant increase in maternal mortality rates, rising from 25.3 to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births between 2018 and 2022. States like Alabama and Mississippi report the highest rates, while California has the lowest. Furthermore, American Indian and Alaska Native women face a mortality rate 3.8 times higher than white women, emphasizing systemic disparities.
What are the leading causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
Cardiovascular disease, cancer, mental and behavioral disorders, and substance-related issues are identified as leading causes of pregnancy-related deaths. These factors, especially cardiovascular disease, highlight the urgent need for better maternal healthcare and postnatal support to improve maternal health outcomes.
How can access to postnatal care reduce pregnancy-related deaths?
Improving access to postnatal care is crucial for addressing late maternal deaths, which are often linked to gaps in healthcare delivery after pregnancy. Enhancing this access can help identify and manage health issues that may arise post-delivery, ultimately improving maternal health outcomes.
What role does racial disparity play in maternal health outcomes?
Racial disparities are significant in maternal health, with non-Hispanic Black and American Indian women experiencing much higher pregnancy-related death rates than white women. This disparity is influenced by differences in access to healthcare, socioeconomic factors, and systemic biases, which necessitate targeted interventions for improvement.
What steps are necessary to improve maternal health outcomes in the U.S.?
To improve maternal health outcomes, it is vital to invest in healthcare infrastructure, ensure equitable access to high-quality pregnancy care, and address the systemic issues contributing to racial and ethnic disparities in maternal mortality and morbidity.
What is meant by late maternal deaths, and why are they significant?
Late maternal deaths refer to deaths caused or worsened by pregnancy that occur between one month to one year postpartum. They signify healthcare gaps between obstetric and primary care, particularly affecting women of color, emphasizing the need for comprehensive maternal healthcare beyond delivery.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. increased nearly 28% between 2018 and 2022, according to a study from JAMA Network Open. |
| The CDC reported 6,283 pregnancy-related deaths during this period, with rates rising significantly across all age groups, especially among those aged 25-39. |
| Pregnancy-related death rates rose from 25.3 per 100,000 live births in 2018 to a peak of 44.1 in 2021, then decreased to 32.6 in 2022. |
| Disparities exist by state, race, and ethnicity; Alabama had the highest rate (59.7) and California the lowest (18.5) per 100,000 live births. |
| American Indian and Alaska Native women faced the highest risks, with rates 3.8 times higher than white women. |
| Cardiovascular diseases were the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, along with cancer and mental health disorders. |
| The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, emphasizing the urgent need for improved maternal health policies. |
Summary
Pregnancy-related deaths have surged in the U.S., with a nearly 28% increase from 2018 to 2022 highlighting critical disparities across various states, races, and ethnicities. This alarming trend, published by JAMA Network Open, indicates a pressing need for enhanced maternal healthcare systems to address the factors contributing to these tragic outcomes. Efforts must focus on equitable access to prenatal and postpartum care to prevent further escalation in pregnancy-related deaths.