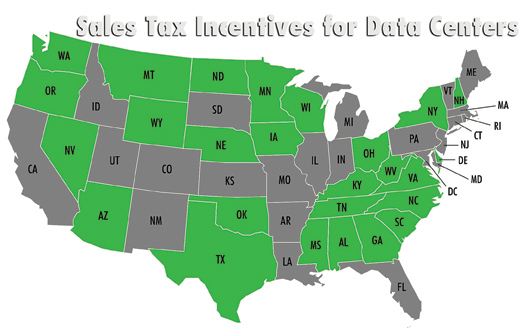
Data center tax incentives have become a driving force in attracting technological investment across the United States. As the demand for cloud-based services surges, states are rolling out lucrative tax breaks for data centers to entice these digital powerhouses, hoping to boost both property and income tax revenue. Lawmakers argue that these incentives are essential to stimulating economic activity, helping local economies thrive while supporting the burgeoning data center industry. However, the hidden costs of these tax breaks—potentially in the billions—raise questions about their long-term viability and impact on state tax revenue. Many economists caution that while data centers offer short-term benefits, the broader economic implications of these subsidies may warrant deeper scrutiny and transparency from policymakers.
Incentives for data storage hubs are rapidly reshaping the landscape of digital infrastructure investment. As cloud computing continues to expand, many states are proactively implementing financial breaks for data facilities, seeking to secure their economic future in the technology sector. These initiatives not only promise immediate fiscal boosts but also aim to create a competitive edge in attracting players within this crucial industry. Nonetheless, some analysts argue that the fiscal advantages of these arrangements may not outweigh the long-term costs incurred by local communities. By examining the economic ramifications of these elaborate agreements, stakeholders can foster a more balanced discourse on the necessity and effectiveness of incentives tailored to the data center ecosystem.
The Rise of Data Center Tax Incentives
In recent years, the emergence of data centers has sparked an intense competition among states looking to attract these vital facilities through enticing tax incentives. As the demand for cloud computing and AI technologies surges, over 30 states have established tax breaks specifically tailored to data center companies. These incentives are marketed as essential tools for economic development, aimed at boosting local job creation and increasing tax revenues. However, critics argue that the necessity and effectiveness of these tax incentives may be overstated, raising questions about their long-term impact on state budgets.
The ripple effect of these tax incentives often leads to significant fiscal challenges for states. For instance, researchers from Good Jobs First have indicated that the financial burdens of these tax breaks can result in billions of dollars in lost state revenue annually, overshadowing any generated income from the data centers themselves. This scenario invites scrutiny regarding the sustainability of such policies and whether the promised economic benefits are truly realized or remain elusive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are data center tax incentives and how do they affect state tax revenue?
Data center tax incentives are financial benefits provided by state governments to attract data centers, encouraging investment and development in their respective areas. These incentives typically include tax breaks like exemptions from property taxes, sales taxes on equipment, or other financial quid pro quo arrangements. While proponents argue that these incentives significantly boost local economies and generate state tax revenue, critics highlight that the lost revenue from tax exemptions often outweighs the gains, especially in cases where data centers do not create substantial local employment or economic activity.
How do tax breaks for data centers impact local economies?
Tax breaks for data centers can offer short-term boosts to local economies through increased property values and potential ancillary investment. However, many economists warn that the long-term fiscal impact may be negative, as these centers often create few jobs relative to their subsidies. Critics assert that while states lose significant tax revenue annually, the actual economic activity generated may not justify the fiscal costs, leading some communities to question whether these tax incentives truly benefit their local economies.
Why do states offer tax incentives for data centers?
States offer tax incentives for data centers primarily to attract investment, stimulate local economic development, and compete in a growing digital economy. The idea is that by providing these fiscal benefits, states can entice data centers to establish operations, which proponents believe will lead to broader economic growth. However, the effectiveness of these incentives is debated, with some studies indicating that many data center businesses would have likely invested in the state even without such tax breaks.
What concerns are associated with data centers and their tax incentives?
Concerns regarding data centers and their tax incentives include potential loss of significant state tax revenue, limited job creation, and environmental impacts. Critics argue that data centers, while generating some local revenue, often do not employ enough workers to offset the cost of tax breaks. Additionally, communities express worries about the infrastructure strain, including electricity and water availability, and the environmental footprint of these facilities, suggesting that the trade-offs for local residents can be unfavorable.
How do data center tax incentives compare across different states?
Data center tax incentives vary widely across states, with some offering extensive tax breaks that can lead to billions in revenue losses while others may impose stricter limitations on such subsidies. For example, states like Georgia and Virginia have crafted competitive incentive packages to attract data centers, resulting in substantial tax waivers. However, the effectiveness and overall economic benefit of these incentives are still under scrutiny, as the long-term impact on state budgets and local economies remains unclear.
What alternatives exist to attract data centers without heavy tax incentives?
Alternatives to attract data centers without relying heavily on tax incentives could include improving local infrastructure, offering workforce development programs, and creating favorable business environments. These approaches could make regions more appealing to data center companies without significant revenue loss from tax breaks. Additionally, investing in sustainable energy solutions can address environmental concerns and position communities as forward-thinking, responsible options for data center establishment.
What is the role of transparency in data center tax incentive agreements?
Transparency in data center tax incentive agreements is crucial for public awareness and accountability. Many tax agreements are often shrouded in secrecy, limiting the ability of policymakers and citizens to assess their financial and social impacts. Increased transparency can help communities understand the potential costs and benefits associated with attracting data centers, ensuring that decisions made reflect the interests of local residents and provide a clear picture of the trade-offs involved.
What can communities do to safeguard their interests when negotiating data center incentives?
Communities can safeguard their interests by advocating for clear terms in tax incentive agreements that include job creation benchmarks, environmental standards, and public reporting requirements. Engaging local governments in the negotiation process to ensure public input and decision-making can also help mitigate potential adverse effects. Additionally, conducting independent economic studies to evaluate the true fiscal impact of proposed data centers can provide necessary data to inform discussions and decisions.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Growing Demand for Data Centers | States offer tax incentives to attract data centers due to their role in cloud storage and AI support. |
| Financial Implications | Some states lose billions annually in tax revenue due to these incentives, which can exceed the revenue generated by the data centers. |
| Debate on Effectiveness | Critics argue that tax breaks are a subsidy to large tech firms that distort economic development and land use. |
| Limited Transparency | Many agreements regarding data centers lack transparency, making it difficult to assess their fiscal impact. |
| Local Impact | Data centers often create few long-term jobs and shift financial burdens to local communities. |
| Counterarguments | Proponents argue incentives are necessary to prevent data centers from relocating and that they align with existing manufacturing exemptions. |
| Concerns in Rural Areas | Although beneficial for local revenues in rural areas, concerns about environmental impact and resource access exist. |
Summary
Data center tax incentives play a pivotal role in the ongoing competition among states to attract technological investments. However, the debate surrounding their economic viability continues to intensify. Although these tax incentives are intended to stimulate growth, questions regarding their overarching benefits versus their fiscal costs have emerged. As data centers proliferate, it’s vital for policymakers and the public to evaluate these incentives critically, ensuring that local communities reap tangible benefits without bearing an undue financial burden.