The China trade war strategies employed by Beijing have created an intricate web of economic interactions that significantly impact U.S. trade relations. As tariffs rise—sometimes exceeding 125% on varied goods—China leverages its robust authoritarian government structure under Xi Jinping leadership to deploy swift, calculated responses. While the tensions disrupt supply chains and challenge the U.S. economy, China’s control over rare earth minerals and aggressive market tactics serve as barriers to American companies seeking to maintain competitive pricing. Furthermore, the Chinese economy’s adaptation to these tariffs illustrates not only resilience but also an innate ability to capitalize on loopholes within global trade agreements. As both nations navigate these tumultuous waters, the need for effective trade negotiations becomes paramount in stabilizing their relationship and addressing mutual economic interests.
In recent years, strategies from China regarding its approach to trade conflicts have evolved into a complex interplay of economic maneuvering. This includes its proactive use of tariffs and trade barriers, as well as a focus on maintaining positive standing with foreign investors and partners. The leadership in Beijing, particularly under Xi Jinping, emphasizes a long-term vision that is often less hindered by the democratic processes found in the U.S. The ongoing challenges in the bilateral trade landscape underscore the necessity for both sides to engage in meaningful dialogue aimed at reducing the escalating tensions. A comprehensive understanding of these alternate approaches to trade challenges highlights the critical importance of diplomatic efforts in fostering stability within global markets.
Understanding China’s Trade War Strategies
China’s trade war strategies reflect its historical resilience and adaptiveness, harnessing both long-term planning and short-term tactics. Chinese leaders are keenly aware that while they can leverage their autocratic decision-making to implement sweeping economic strategies quickly, these methods come with risks. For instance, retaliatory tariffs against the U.S. can significantly impact their economy, prompting many analysts to question the sustainability of maintaining high tariffs on products essential for U.S. markets. Moreover, the notion of ‘eating bitterness’ now seems outdated as the Chinese population’s expectations continue to rise, creating pressure for the Communist Party to improve, rather than revert, living standards of its citizens.
On the flip side, recent trends show China may be shifting its strategies in response to changing economic dynamics. The ongoing trade negotiations reveal that while Beijing could impose high tariffs—potentially as high as 125%—doing so could also deter foreign investment crucial for its economic growth. These decisions are not merely unilateral but involve intricate deliberation among party officials, showcasing a more nuanced approach under Xi Jinping’s leadership. In essence, while China might have immediate tools at its disposal, strategic long-term thinking plays a vital role in their ongoing trade negotiations with the U.S.
Impact of Tariffs on U.S. Trade Relations with China
The escalating tariffs imposed by the U.S. on Chinese imports have created a ripple effect in global trade relations. With tariffs reaching as high as 125% on various products, such as electronics and consumer goods, American consumers are starting to feel the pressure. The backlash from local businesses is palpable, as many companies have reported increased costs leading to higher prices for consumers. Economists assert that a prolonged period of elevated tariffs could push the U.S. toward a recession, further complicating its trade relations not only with China but also with other nations that sell goods to the U.S.
In this environment, the stakes are high for both nations. The Chinese economy, with its reliance on exports, is at risk of considerable long-term damage if negotiations fail. The U.S., meanwhile, faces the challenge of balancing domestic interests with international economic pressures. The effect of tariffs extends beyond simple economics into the social fabric of both countries, with lower-income families disproportionately bearing the burden. This evolving trade landscape necessitates a reevaluation of U.S. trade relations, pushing for a more strategic, dialogue-driven approach that could foster a resolution beneficial for all involved.
Xi Jinping’s Leadership in Trade Negotiations
Xi Jinping’s leadership style plays a pivotal role in shaping China’s approach to trade negotiations with the U.S. Unlike previous leaders, Xi emphasizes consensus-building among party officials, which can lead to more stable yet sometimes slower decision-making processes. This contrasts sharply with Donald Trump’s more erratic approach, where tariffs can be levied at a moment’s notice. Xi understands that China’s future economic growth is inextricably linked to how well it navigates these turbulent waters of international trade, especially amidst rising tariffs and tensions.
Moreover, under Xi’s leadership, China has sought to position itself as a formidable competitor on the global stage. While the immediate goal may revolve around mitigating the impact of U.S. tariffs, the long-term strategy includes bolstering domestic industries and diversifying trade partnerships. This includes investing in regional agreements and looking towards markets in Africa and Europe, thereby reducing reliance on a single economic partner. Thus, Xi’s strategic foresight in trade negotiations reveals both a defensive and offensive posture, as he aims to ensure China’s economic stability amid ongoing challenges.
The Role of Tariffs in Economic Pressure
Tariffs serve as a powerful tool in the broader context of economic pressure from the U.S. on China. The imposition of tariffs has not only affected Chinese exports to the U.S. but has also informed global perceptions regarding tariff instability. Such actions send ripples through the supply chains, leading many companies to reconsider their manufacturing strategies. For China, the ramifications of significant tariff hikes can potentially stifle crucial economic sectors, prompting policymakers to rethink their dependency on U.S. market access.
Furthermore, the increasing tariffs provoke a psychological effect on both American and Chinese business leaders alike. The uncertainty surrounding trade negotiations creates hesitancy in investment decisions, impacting how corporations plan for the future. This unease can result in reduced economic activity and potential job losses, further elevating the stakes for both nations involved. Consequently, the strategic discourse surrounding tariffs is as much about psychological positioning as it is about economic metrics.
Financial Implications of Trade War Strategies
The financial strategies employed by China during the trade war reveal a nuanced understanding of global markets. One tactic has been to subtly devalue the yuan to offset the increasing tariffs on Chinese goods. However, such a strategy is fraught with complications. A significant devaluation might lead to heightened inflation and a loss of confidence among consumers, prompting them to convert yuan into more stable currencies like the dollar or euro. As a result, while short-term financial maneuvering may provide some relief from tariffs, the long-term consequences could destabilize the Chinese economy.
Moreover, China’s vast holdings of U.S. Treasury bonds add another layer of complexity to its financial strategy. Selling off these bonds could trigger a spike in U.S. interest rates, further complicating economic relations. Such a move risks strengthening the dollar, making Chinese exports even more expensive and potentially exacerbating the trade imbalance. The interplay of these financial strategies illustrates that while China possesses powerful tools, the ripple effects of their use could lead to unintended consequences that threaten their overall economic stability.
Consumer Impact of Tariffs and Trade Policies
The proliferation of tariffs has direct implications for consumers, particularly in the U.S. The introduction of high tariffs on Chinese goods has increased prices and limited choices available in the market. This consumer impact is most palpable among lower-income households, which tend to spend a higher percentage of their income on essential goods. As prices soar due to tariffs, these families face even greater economic strain, leading to broader questions about the morality and efficacy of trade policies that disproportionately affect the vulnerable populations.
Additionally, the shifting landscape of consumer goods can reshape purchasing behaviors. With the possibility of reduced availability of affordable Chinese imports, consumers may look to alternative sources or products that are less affected by tariffs. This shift could lead to changes in brand loyalty and consumer preferences, as individuals adapt to the new economic realities. As such, understanding consumer impact is critical for policymakers as they navigate the complex terrain of trade relations.
Anticipating Future Trade Negotiations
Looking ahead, the complexities of U.S.-China trade negotiations suggest that both nations will need to adopt more collaborative strategies. Economic indicators point to a mutual recognition that continued tariffs could hurt both the U.S. and Chinese economies, prompting a more cooperative approach. China’s readiness to engage in dialogue signals an opportunity for fresh negotiations, aiming to reach a compromise that benefits both sides without undermining their respective economies.
The approach to future negotiations may also be influenced by changing political landscapes within both countries. For instance, the potential shift in U.S. administration and its foreign policy could impact strategies used in addressing trade relations with China. Leaders from both nations must weigh their priorities carefully, as the political repercussions of failing to reach a satisfactory agreement could be substantial, not only economically but also on the global stage.
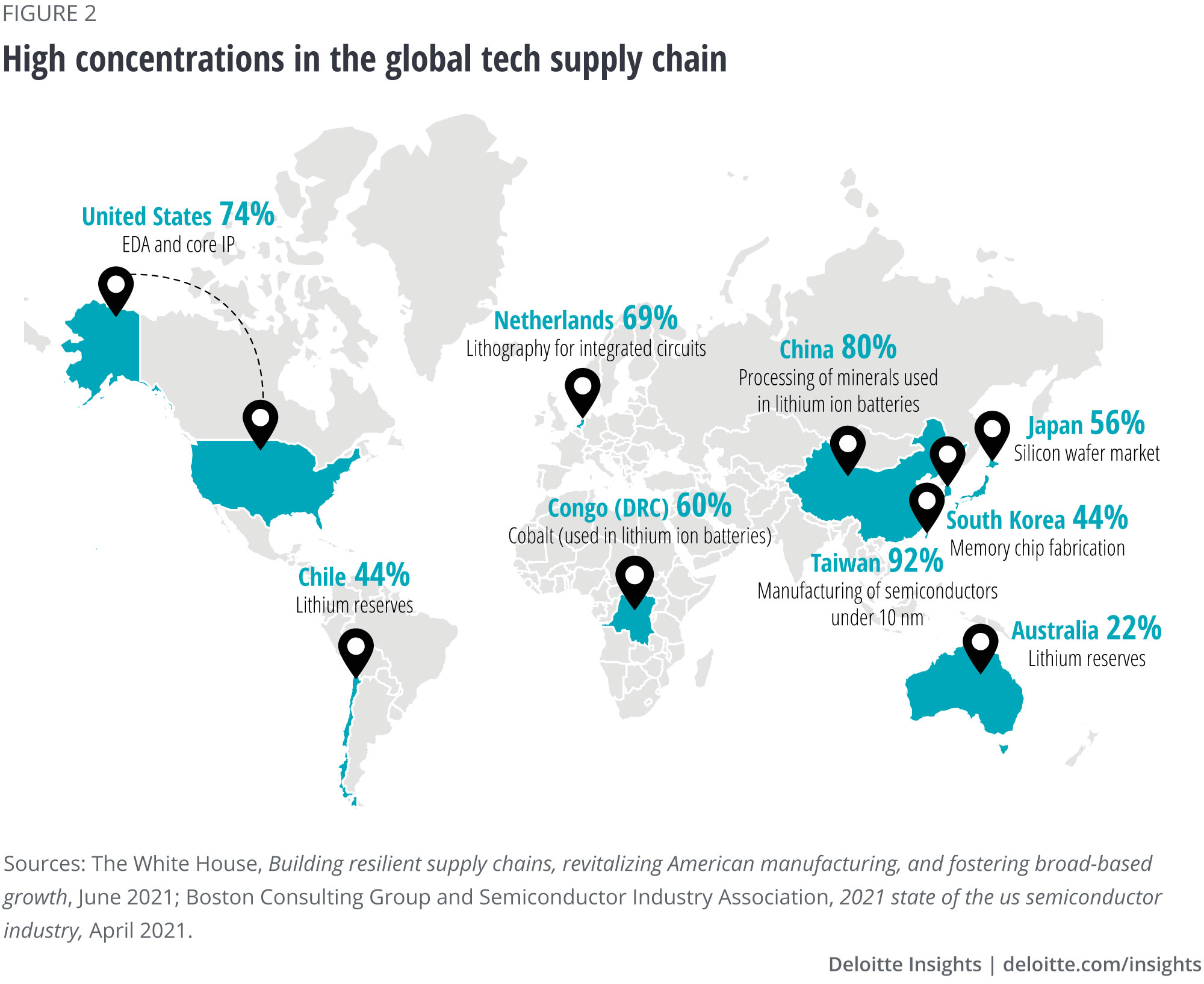
Rare Earths and Their Strategic Importance
China’s control over rare earth elements presents both a strategic advantage and a potential vulnerability in trade negotiations with the U.S. These minerals are vital for various industries, including technology and defense. By leveraging its dominance in rare earths, China can apply pressure in trade negotiations. However, doing so also risks incentivizing other countries to develop alternative sources, potentially undermining China’s market position in the future.
Additionally, U.S. businesses have been aware of the risks associated with reliance on Chinese rare earths, prompting discussions around diversification of supply chains. As firms seek to secure their operations from trade uncertainties, they may invest in mines and processing facilities elsewhere, which could increase competition for China in the global market. Thus, while China currently holds a significant strategic position, the dynamics surrounding rare earths may quickly evolve as nations reassess their dependencies amid rising trade tensions.
The Psychological Dimension of the Trade War
One often overlooked aspect of the trade war is the psychological impact it has on both consumers and business leaders in the U.S. and China. The narrative of enduring hardships, often referenced in analyses of the Chinese approach, paints a picture that could lead to nationalistic feelings influencing economic decisions. In periods of heightened tension, messages from government leaders about resilience and self-sufficiency can reinforce a resolve among consumers and businesses to support domestic products, impacting long-standing trade habits.
On the other hand, American consumers are grappling with the implications of tariffs entwined in their everyday spending. As prices rise, the narrative around tariffs becomes less about abstract economic policies and more personal, affecting how consumers perceive both their government and the principles of free trade. This psychological interplay shapes not only consumer behavior but also public opinion, impacting the broader trade policies and negotiations moving forward.
The Imperative for Cooperative Trade Relations
The ongoing U.S.-China trade war underscores the necessity for cooperative trade relations that can mitigate economic fallout. The contrasting approaches of negotiation between China’s state-driven model and America’s market-driven tendencies present a unique challenge. Both nations can no longer afford a trade war characterized by harsh tariffs that create synchronous economic pain, as evidenced by the backlash from consumers and businesses alike.
In seeking long-term solutions, strategies must pivot towards collaboration rather than confrontation. Both the U.S. and China could benefit from establishing frameworks that encourage dialogue, address mutual interests, and foster a more predictable trading environment. This shift could diminish the adversarial nature of their relationship, leading to an era of constructive engagement that benefits not only the two nations involved but also the global economy at large.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key strategies China employs to navigate trade war tariffs?
China employs a variety of strategies to navigate trade war tariffs, including raising tariffs on U.S. goods, imposing regulations on U.S. companies operating in China, and utilizing its control over critical minerals and rare earths. Additionally, Beijing can manipulate its currency to make exports more competitive despite high import tariffs. However, each strategy comes with risks that could impact the Chinese economy.
How do China tariffs impact U.S. trade relations?
China tariffs significantly impact U.S. trade relations by increasing the cost of imports, which can lead to higher prices for American consumers and potentially drive the U.S. into a recession. The high tariffs also encourage U.S. companies to lobby for relief, creating pressure for negotiations between the two nations. Furthermore, these tariffs can lead to retaliatory measures from China, complicating U.S. trade relations even further.
How does Xi Jinping’s leadership influence China’s trade war strategies?
Xi Jinping’s leadership influences China’s trade war strategies by promoting a unified approach and ensuring that decisions reflect the consensus of senior party officials. This structured decision-making process contrasts with the more unpredictable U.S. environment, where tariffs can be changed unilaterally. Xi’s government is focused on maintaining economic stability, so strategies may include balancing domestic pressures with aggressive trade negotiations.
What are the long-term implications of the trade negotiations between the U.S. and China?
The long-term implications of trade negotiations between the U.S. and China can affect global trade dynamics, supply chains, and international economic stability. Successful negotiations could lead to reduced tariffs and improved U.S.-China trade relations, while failure could result in prolonged economic strain for both nations. Additionally, such outcomes can establish precedents for how future trade disputes are handled internationally.
What role do U.S. companies play in the China trade war strategies?
U.S. companies play a crucial role in China trade war strategies as they are often caught in the crossfire of tariffs and sanctions. The pressure from high tariffs may motivate these companies to lobby for policy changes in Washington, influencing trade negotiations. Additionally, any adverse effects on their operations can lead to significant economic implications, impacting jobs and investments in both countries.
How does the Chinese economy adapt to increased U.S. tariffs?
The Chinese economy adapts to increased U.S. tariffs by exploring alternative markets and diversifying exports. Additionally, China may also bolster its domestic consumption to mitigate reliance on U.S. trade. A strategic approach includes negotiations with other global partners and investments in technology to reduce dependence on affected sectors.
What are some countermeasures China could use against U.S. trade pressure?
China could implement several countermeasures against U.S. trade pressure, including retaliatory tariffs, regulatory crackdowns on U.S. businesses, currency adjustments, and leveraging its dominance in rare earths. Other measures include seeking trade agreements with other nations to divert trade flows and mitigate the impact of U.S. tariffs.
Can China maintain its economic growth amid trade war challenges?
China can maintain its economic growth amid trade war challenges by leveraging its vast consumer market, investing in technology and innovation, and strengthening trade relations with other countries. While tariffs may hinder growth in certain sectors, a robust domestic economy and diversified trade strategies can help sustain overall economic performance.
| Key Points |
|---|
| China relies on political endurance and a centralized decision-making process, viewed favorably compared to the U.S.’s democratic processes. |
| The perception that China’s government can make quick decisions is misleading; it faces significant bureaucratic processes. |
| Trump’s tariffs give him unilateral power, contrasting with China’s requirement for party consensus in decision-making. |
| China can increase tariffs to respond to U.S. tariffs, impacting trade volume significantly, but risks economic repercussions. |
| Strategies like targeting U.S. companies through investigations might backfire by reducing foreign investment in China. |
| China’s control over rare earth minerals is limited; they may lose market control instead of gaining leverage against the U.S. |
| Currency devaluation can help but may lead to significant capital outflows and increased import costs. |
| Both countries face economic harm from tariffs, suggesting a potential for negotiated resolution to the trade conflict. |
| Tariff strategies lead to unexpected consequences, including incentivizing Chinese exports through third countries to avoid tariffs. |
Summary
China trade war strategies are complex and multifaceted. While they embody a resilient approach to endure pressure from the U.S., the reality is that these strategies carry risks that could exacerbate economic challenges within China. Recent moves by both nations suggest that a prolonged economic battle could lead to significant losses. Considering these factors, it is crucial for both the U.S. and China to seek diplomatic solutions to mitigate the impacts of tariffs and ensure stable economic conditions for their populations.